Facility Accessibility Design Standard

Important Notice
This Facility Accessibility Design Standard is published as a DRAFT and is being published in stages for review and consultation purposes only. It has not been approved or adopted by City Council and does not represent current City policy, standards, or requirements. The content is subject to change and should not be relied upon for design, construction, procurement, or compliance decisions at this time.
We would like to acknowledge and thank the City of London for permission to adopt the 2021 London Facility Accessibility Design Standard and the Windsor Accessibility Advisory Committee for their guidance and support on this project. In particular, we are grateful for the remarkable energy, time, and expertise provided by the FAD Subcommittee. They have contributed, through their lived experience and architectural expertise, to one of the few accessible FAD standards in Ontario and one of the few standards to directly incorporate recommendations from persons with disabilities.
FAD Subcommittee Members
Mark Keeler(Chair) / Accessibility Officer
Peter Best (Co-Chair)
Surendra Bagga
Ricardo Pappini
Nicholas Petro
Caleb Ray
Chapter 1 Introduction
The Windsor Facility Accessibility Design Standard serves to provide design standard guidance and best practices for the design and construction of new facilities and renovation or retrofitting of existing facilities owned, operated, and maintained by the City of Windsor. Such guidance and principles address the needs of persons with a comprehensive range of disabilities. The accessibility design standards is based on the concept of universal design that focuses on the development of environments and products that are usable by the full spectrum of people regardless of their ability without adaptation or specialized design. This concept is enshrined in seven design principles listed in Section 1.1.1.
Architects, engineers, staff, and professionals use FADS to enhance accessibility beyond the minimal requirements of the Ontario Building Code and the Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act, 2005. Adopted with permission from the 2021 London Accessibility Design Standard, this standard shall be used when planning and designing municipal facilities in a concerted and ongoing effort to remove and prevent barriers for people with disabilities. In the event of conflicts of requirements occur with other standards or legislation; the most accommodating requirements should apply but never less than the current building code or AODA thresholds.
| This standard incorporates the belief in universal design that recognizes the broad diversity of people who use facilities. Universal design is defined as: “The design of products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design” (Source: North Carolina State University 1997). The universal design philosophy are structured around the seven Design Principles |
|
Application
The requirements of this standard shall be:
- Mandatory for all newly constructed and retrofitted facilities owned, leased or operated by the City of Windsor; and
- Encouraged for all other facilities, whether new or retrofitted.
All areas of newly designed or newly constructed facilities and altered portions of existing facilities shall comply with Sections 2 to 5, unless otherwise provided in this section or as modified in Section 6.The specific facility types listed in Section 6 shall, in addition to all of the provisions specified in Sections 2 to 5, comply with the additional design requirements specified in Section 6.
Where a facility contains more than one use covered by a special application section, each portion shall comply with the requirements for that section in addition to all other general provisions. All facilities shall be accessible for employees, as well as patrons and other users. All areas intended for use by employees shall be designed and constructed to comply with this standard.
This standard applies to temporary facilities, as well as permanent facilities.
Exceptions
The requirements of Sections 2 to 5 do not apply to:
- service rooms;
- elevator machine rooms;
- janitor rooms;
- service spaces;
- crawl spaces;
- attic or roof spaces;
- residential occupancies
- buildings of Group F Division 1 occupancy, as defined by the Ontario Building Code (latest edition with all amendments); and
- buildings which are not intended to be occupied on a daily or full- time basis, including, but not limited to, automatic telephone exchanges, pump houses and substation
1.2.1 Retrofitting, Alterations, and Additions
Application of these standards related to retrofitting, alterations and additions also requires the following:
- Each addition to an existing facility shall be regarded as an alteration;
- Each space or element added to the existing facility shall comply with the applicable provision(s) of this standard;
- Except where the provision of accessible features is technically infeasible, no alteration shall decrease or have the effect of decreasing accessibility or usability of an existing facility to below the requirements for new construction at the time of alteration;
- If existing elements, spaces or common areas are altered, then each such altered element / space / feature / area shall comply with all applicable provisions. If the applicable provision for new construction requires that an element / space / feature / area be on an accessible route and the altered element / space / feature / area is not on an accessible route, this route shall be altered to become accessible;
- If alterations of single elements, when considered together, amount to an alteration of a room or space in a facility, the entire space shall be made accessible;
- No alteration of an existing element, space or area of a facility shall impose a requirement for greater accessibility than that which would be required for new construction;
- If an escalator or stairs are proposed as a means of access where none existed previously, and major structural modifications are necessary for such installations, then a means of accessible access shall also be provided;
- If a planned alteration entails alterations to an entrance, and the facility has an accessible entrance, the entrance being altered is required to be accessible;
- If the alteration work is limited solely to the electrical, mechanical or plumbing system, hazardous material abatement, automatic sprinkler retrofitting, and does not involve the alteration of any elements or spaces required to be accessible under these standards, then this standard does not apply (except for alarms and assistive listening systems);
- An alteration that affects the usability of or access to an area containing a primary function shall be made to ensure that, to the maximum extent feasible, the path of travel to the altered area, the washrooms and drinking fountains serving the altered area are readily accessible to and usable by individuals with disabilities; and
- Where the provision of accessible features is technically infeasible, and the standard allows a reduction of maneuvering space from the requirements for new construction, the reduced dimensions are minimums. Where possible, larger maneuvering spaces must be provided.
1.2.2 Heritage Facilities
This standard will apply to alterations to a heritage facility, however, under the Ontario Human Rights Code, there are allowances for modification to the defining features of a heritage facility which are deemed to alter the essential nature or substantially affect the viability of the enterprise. Public heritage facilities should be assessed for compliance to accessibility standards on an individual basis, to determine the most effective and least disruptive means of retrofit, where required. Consider the following general guidelines:
- Facilities and / or areas that are generally used independently by the public and have undergone extensive modernization should be permanently and fully accessible. This includes parking areas, reception areas, washrooms, food service areas and gift shops. It can also include walkways and garden areas. If accessibility is limited by non-heritage elements, those elements should be revised;
- Facilities and / or areas which are used only by guided tour groups, through which assistance could easily be provided to open doors or to place a temporary ramp, could remain as existing or with minor temporary modifications;
- It is desirable to provide a complete experience of a public heritage facility. If an accessible area or areas can be provided to fully experience a given site or facility context, access to the entire site or facility is not necessary; and
- Access to above-grade and below-grade areas is not necessary if the context of those areas can be adequately provided on the accessible floor level.
If the retrofit for accessibility of a main public entrance in a heritage facility would substantially threaten or destroy the historic significance of the facility, access shall be provided at an alternative entrance with directional signs at the main public entrance. The accessible entrance should have a notification system (if not generally used by the public) and remote monitoring (if security is an issue). Safe egress from a heritage facility is required.
1.2.3 Equivalent Implementation
In a retrofit situation where the requirements of a section of this standard are technically infeasible to implement, equivalent facilitation may be proposed. Equivalent facilitation proposals shall be referred to the appropriate departmental leader.
1.2.4 Implementation
The City departments, as well as contracted consulting firms shall be responsible for the application of the 2025 Facility Accessibility Design Standards, when designing and administering all construction and renovation projects associated with new facilities, as well as the retrofit, alteration or addition to existing facilities, owned, leased or operated by the City of Windsor. Designing and constructing to this standard shall be included as a mandatory requirement in all City of Windsor Request for Proposals, Tender Documents and Construction Contracts.
1.2.5 Enforcement - Which department should be set here?
The Facilities Design and Construction Division of the City of Windsor and other City departments, through the project management function, shall ensure compliance to this standard during the pre-planning, design, construction documents preparation and contracts administrative phases.
Application
The dimensions and maneuvering characteristics of wheelchairs, scooters and other mobility devices are as varied as the people who use them. Traditionally, accessibility standards have taken a conservative approach to wheelchair maneuverability, reflecting the needs of a physically strong individual using a manual wheelchair. Such an approach excludes the many users without such a degree of strength or those using a larger mobility device.
This standard more accurately reflects the vast array of equipment that are used by persons to access and use facilities, as well as the diverse range of user ability. This standard incorporates more generous space requirements, particularly related to the dynamic movement of people using wheelchairs, scooters or other assistive devices.
Space and reach provisions for persons who use wheelchairs, scooters and other mobility devices shall comply with this section1.3.1 Clearance and Turning Space Requirements
A minimum clear floor / ground space and turning space is required to accommodate diverse users and types of mobility aids. These requirements are consistently applied throughout this standard, applicable for both exterior and interior environments including a “universal” clear floor / ground space and a suitably dimensioned clear turning space / circle for users of mobility aids, as follows:
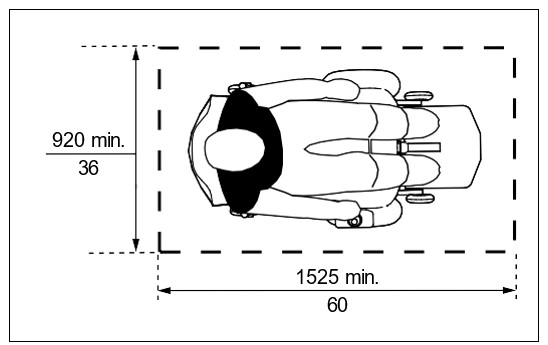
a) minimum clear floor / ground space of 920 mm by 1525 mm ( 36 in by 60 in) for a single wheelchair or scooter for forward or parallel approach to an object (Figure i). Clear floor / ground space for wheelchairs may be part of the knee space required under some objects; or
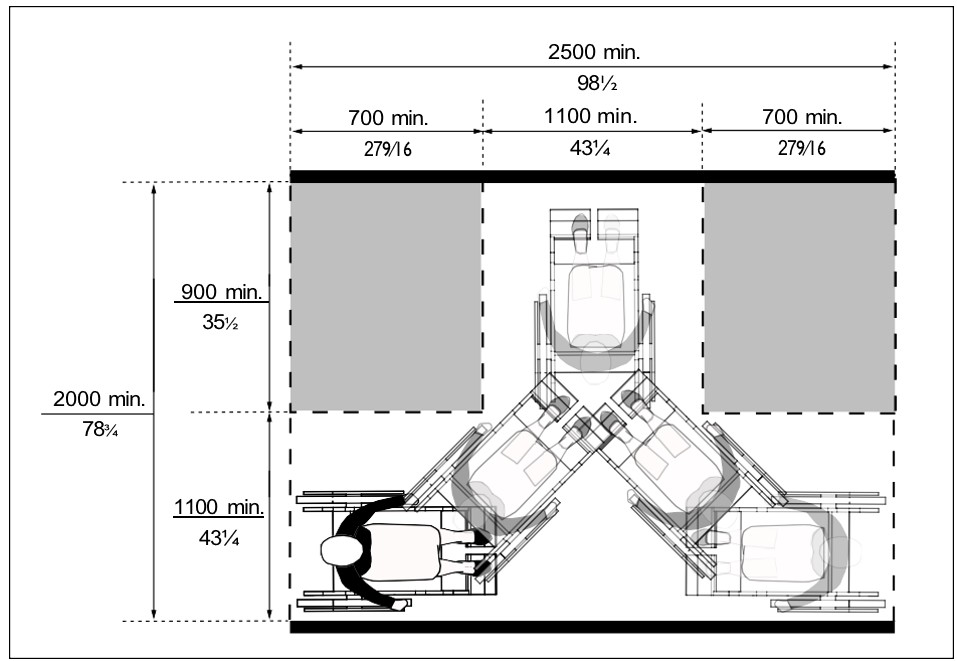
b) turning space of 2440 mm (96 in) in diameter for users of mobility aids to make a 360-degree turn (Figure ii) or various required clearances for a 180-degree turn (Figure iii).
 |
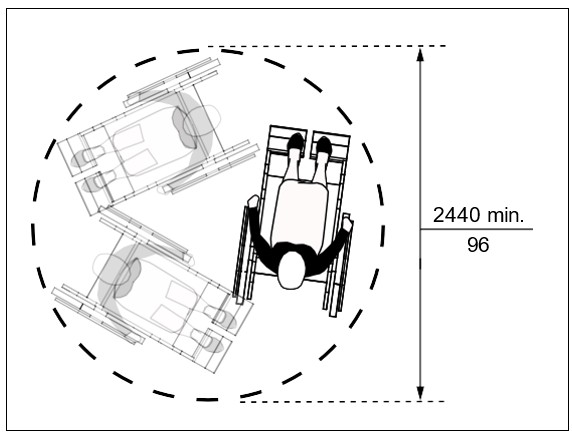 |
| Figure i: Universal Clear Floor / Ground Space for Mobility Devices | Figure ii: 360° Turning Space / Circle |
 |
|
| Figure iii: 180° Turning Space |
|
1.3.2 Clearances at Alcoves
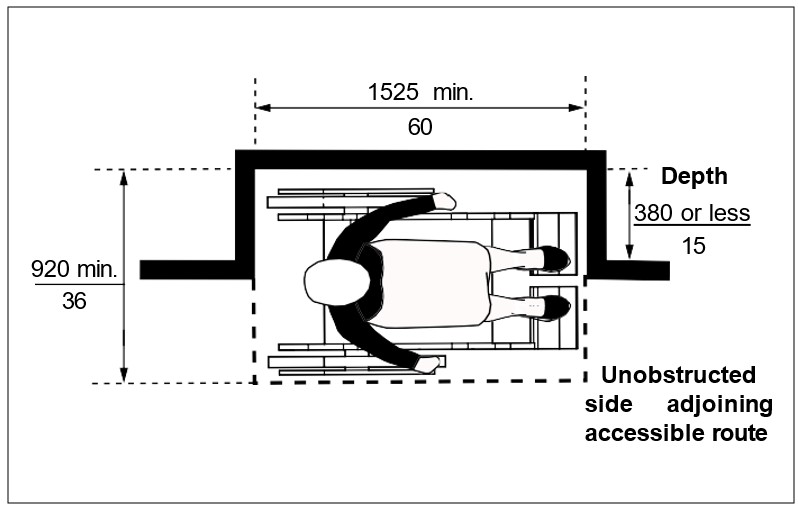
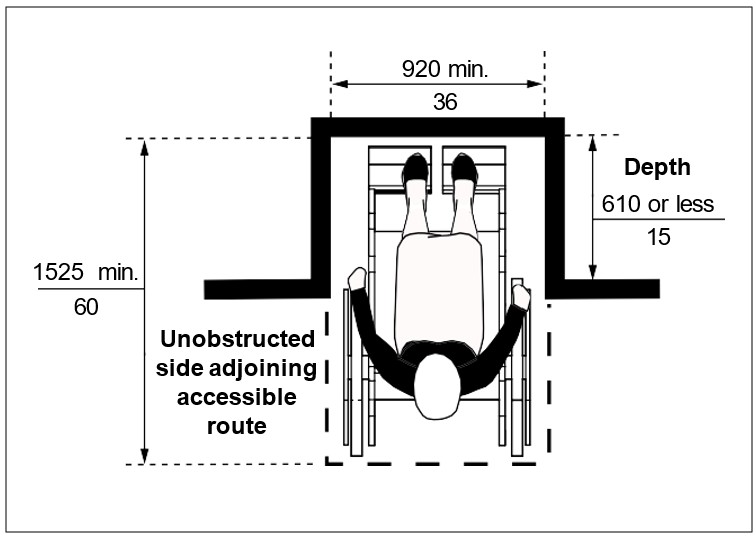
One full, unobstructed side of the clear floor space or ground space for a wheelchair or scooter shall adjoin or overlap an accessible route or adjoin another clear floor space for mobility aids. If a clear floor space is located in an alcove or otherwise confined on all or part of three sides, additional maneuvering clearances is required as shown in Figures iv, v, vi, and vii.
 |
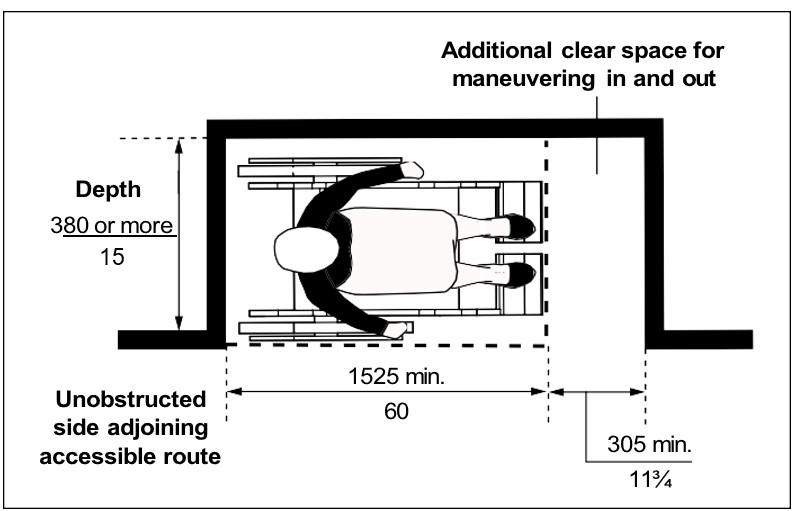 |
| Figure iv: Clearances at Alcove - Side Approach where Depth of Alcove is 380 mm (15 in) or less | Figure v: Clearances at Alcove - Side Approach where Depth of Alcove is more than 380 mm (15 in ) |
 |
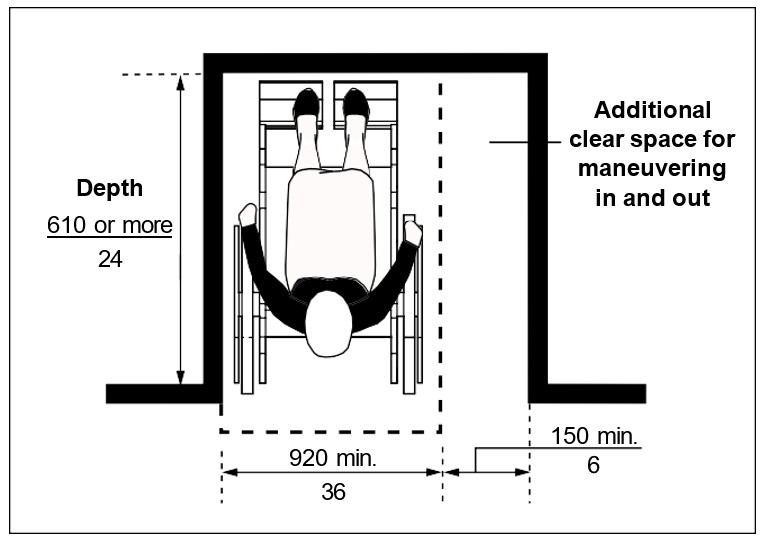 |
| Figure vi: Clearances at Alcove - Front Approach where Depth of Alcove is 610 mm (24 in) or less | Figure vii: Clearances at Alcove - Front Approach where Depth of Alcove is more than 610 mm (24 in ) |
1.3.3 Reach Requirements
The following requirements relate to minimum and maximum reach ranges, based on a forward (frontal) or a side (parallel) approach to an object, element or feature. This includes consideration for whether the reach is without an obstruction, or whether it is over an obstruction. Additionally, reach range related specifically to touching versus grasping an object, element or feature is addressed where there is a side or forward approach over an obstruction
| Best Practice
Despite these requirements, optimal reach range identified in other sections of these standards is 900 to 1100 mm (35½ to 43¼ in), for either side or frontal approach, when obstructed or when there is no obstruction. Additionally, the Ontario Building Code requires all controls for the operation of facility services to be mounted at a maximum of 1200 mm (47 in) above the finished floor for thermostats or manual fire pull stations and 900 to 1100 mm (35½ to 43¼ in) for all. |
1.3.3.1 Forward Reach: No Obstruction
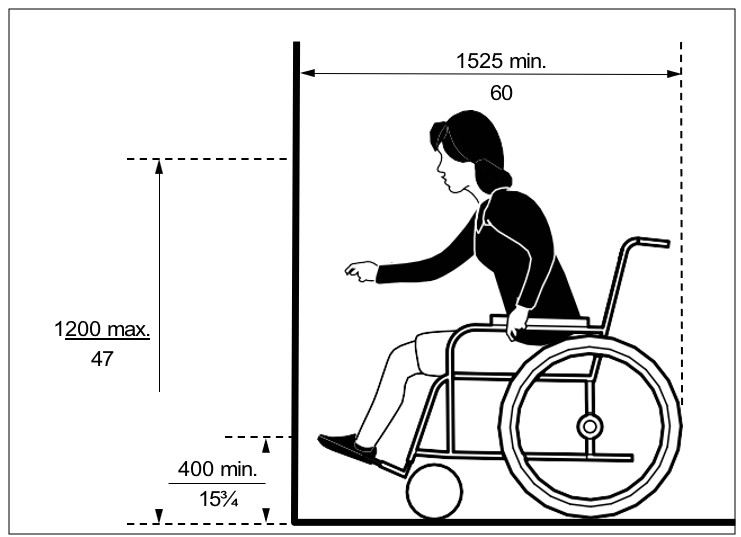
Where a minimum clear floor space of 920 mm (36 in) wide by 1525 mm depth (60 in) allows a forward approach to an object, feature or element, with no obstruction, provide: (Figure viii)
a) maximum high forward reach of 1200 mm (47 in) above finished floor ; and
b) minimum low forward reach of 400 mm (15¾ in) above finished floor.
1.3.3.2 Forward Reach: With Obstruction
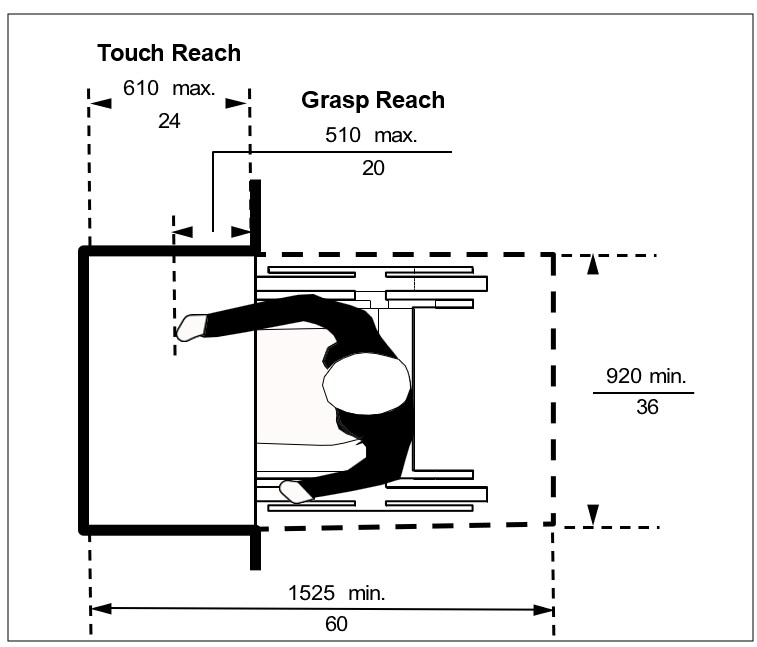
Where a minimum clear floor space of 920 mm (36 in) wide by 1525 mm depth (60 in) allows a forward approach to an object, feature or element, with an obstruction, provide: (Figures ix and x)
a) maximum high forward reach of 1100 mm (43¼ in) above finished floor, with a maximum depth for touch reach at 610 mm (24 in); or
b) maximum high forward reach of 1100 mm (43¼ in) above finished floor, with a maximum depth for grasp reach at 510 mm (20 in).
 |
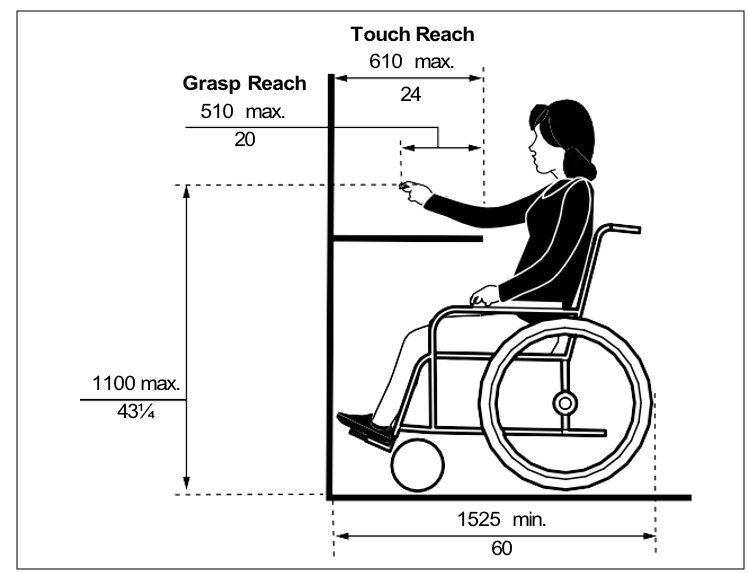 |
| Figure viii: Forward Reach - No Obstruction | Figure ix: Forward Reach over an Obstruction - Section View |
 |
|
| Figure x: Forward Reach over an Obstruction - Plan View |
|
1.3.3.3 Side Reach: No Obstruction
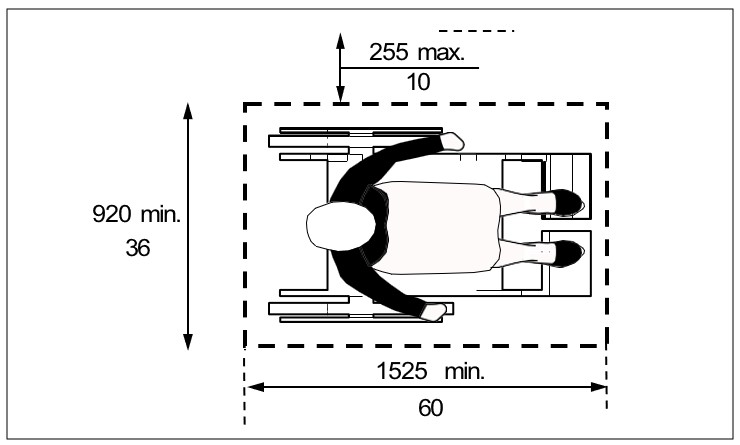
Where a minimum clear floor space of 920 mm (36 in) wide by 1525 mm depth (60 in) allows a side approach to an object, feature or element, with no obstruction and with a maximum reach depth of 255 mm (10 in), provide: (Figures xi and xii)
a) maximum high side reach of 1370 mm (54 in) above finished floor; and
b) minimum low side reach of 230 mm (9 in) above finished floor.
1.3.3.4 Side Reach: With Obstruction
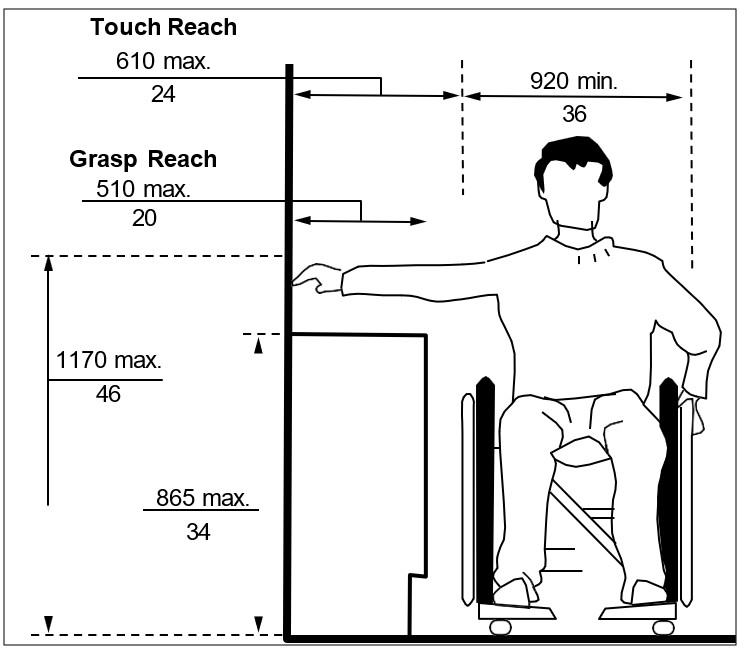
Where a minimum clear floor space of 920 mm (36 in) wide by 1525 mm depth (60 in) allows a side approach to an object, feature or element, over an obstruction that is maximum height of 865 mm (34 in), provide: (Figure xiii)
a) maximum high side reach of 1170 mm (46 in) above finished floor, with a maximum depth for touch reach at 610 mm (24 in); or
b) maximum high side reach of 1170 mm (46 in) above finished floor, with a maximum depth for grasp reach at 510 mm (20 in).
 |
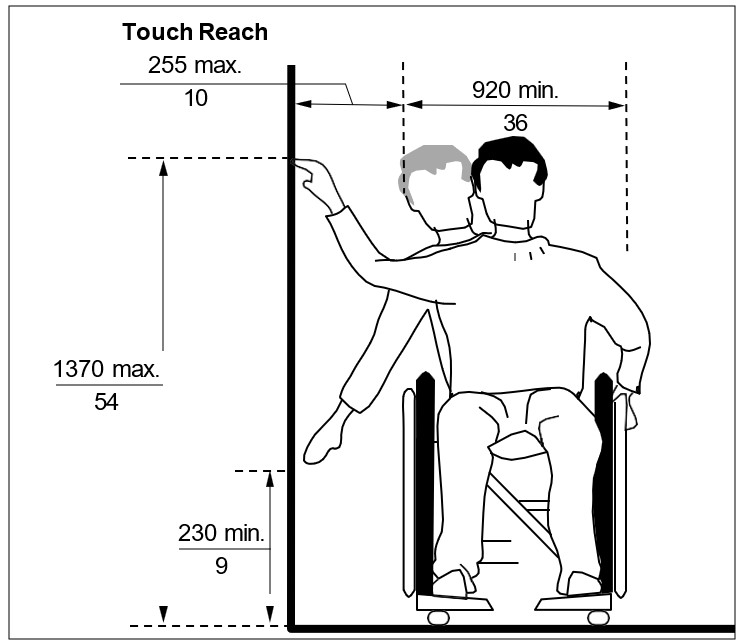 |
| Figure xi: Side Reach - No Obstruction - Plan View | Figure xii: Side Reach - No Obstruction - Section View |
 |
|
| Figure xiii: Side Reach over an Obstruction - Section View |
|
1.41 Standard Organization
These standards are organized to provide accessibility criteria in the following sections, in order to group and identify issues that are related. These sections are identified as follows:
| 1.0 | Introduction |
| 2.0 | Common Elements |
| 3.0 | Exterior Elements |
| 4.0 | Interior Elements |
| 5.0 | Systems, Controls, and Communications |
| 6.0 | Special Facilities and Spaces |
| 7.0 | Tables, Charts, Figures, and Glossary |
These sections are further divided into additional subsections that refer to specific site or facility elements. At the start of each section, the “Application” of the standards is identified to assist with implementation and how each section relates or applies to the built environment, element or feature
1.4.2 Dimensions
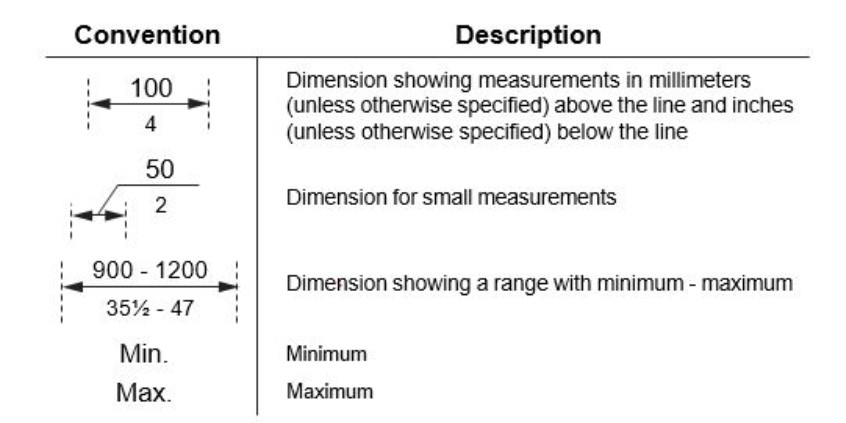
The dimensions for specific accessibility criteria are stated in millimeters (mm) or meters (m) throughout this document, rounded up to the nearest multiple of five. Measurements in inches (in) or feet (ft) are provided adjacent to metricmeasurements in brackets, for example 1525 mm (60 in), and are converted from the metric measurement. Where metric measurements are too small or specific, imperial conversion is not provided in order to maintain accuracy. Dimensions that are not marked as “maximum” or “minimum” are absolute, unless otherwise indicated. All dimensions for construction purposes are subject to conventional industry tolerances. Dimension conventions for diagrams are as follows:
1.4.3 Tables, Figures, and Graphs
Throughout these standards, several tables, figures and graphics are provided to assist the user with understanding the application of the accessibility criteria and design issues under consideration. These are summarized in the Appendices under Section 7.1 Tables, Figures, and Graphs
Throughout this document, terminology may be used that may not be familiar or understood. For the purposes of this standard, words and terms have their meanings defined in Section 7.2 Glossary
The City of Windsor recognizes that accessibility best practices continue to evolve and change over time, with the expectation that these standards are recognized as a “living document” and will be updated on a regular basis. Feedback from the public, city administration, and vendors may be directed to accessibility@citywindsor.ca
Access Aisle - Access aisles refer to an accessible and safe pedestrian space or route used for loading and unloading from the vehicle and safe travel to and from designated accessible parking spaces to the nearest accessible route/entrance. Access aisles include pavement markings for easy identification and are often shared between accessible parking spaces.
Accessible - Refers to any space, feature, element, site, environment, or facility that can be used (e.g., located, approached, entered, exited, or operated) by people with varying disabilities, with or without mobility aids or assistive devices. It can also refer to services, practices, and programs.
Accessible Element - An element specified by this standard (for example, telephone, controls etc.).
Accessible Route - A continuous, unobstructed path (interior or exterior) connecting users to accessible elements, features, amenities, and spaces. Typically, accessible routes include parking access aisles, pedestrian sidewalks and curb ramps, and interior corridors, floors, elevators, and ramps.
Accessible space - Space that complies with this standard
Accommodation - A term used to reflect how an individual’s needs are met for unique circumstances where a solution may not be “technically” feasible or practical to implement. Where barriers continue to exist because it is impossible to remove those barriers at a given point in time, then accommodation should be provided to the extent possible, short of “undue hardship”. There is no set formula for accommodating people with disabilities. Each person's needs are unique and must be considered afresh when an accommodation request is made. A solution may meet one person's requirements but not another's, although it is also the case that many accommodations will benefit large numbers of persons with disabilities.
Adaptable - The ability of a certain building space or element, such as kitchen counters, sinks, or grab bars, to be added or altered so as to accommodate the needs of individuals with or without disabilities or to accommodate the needs of persons with different types or degrees of disabilities.
Addition - An expansion, extension, or increase in the gross floor area of a facility.
Alteration - A change to a facility that affects or could affect the usability of the facility or part thereof. Alterations include but are not limited to, remodeling, renovation, retrofitting, rehabilitation, reconstruction, historic restoration, resurfacing of circulation paths or vehicular ways, changes or rearrangement of the structural parts or elements, and changes or rearrangement in the plan configuration of walls and full-height partitions. Normal maintenance, painting or wallpapering, or changes to mechanical or electrical systems are not alterations unless they affect the usability of the building.
Ambient Light - The total amount of light in a space, including daylight or artificial light, whether from direct sources or reflected from surfaces in that space.
Amenities - Features or services that are usable by the public that typically increases physical comfort throughout the built environment (e.g., washrooms, resting areas, telephones, drinking fountains, or food vending machines).
Amenity Strip - A section of a path or sidewalk that is set aside for placement of street furniture (e.g., benches, hydro poles, vending machines, and post boxes), to ensure it is located away from the pedestrian path of travel.
Anthropometrics - Refers to the study of human physical measurement, movement, and proportions of the human body, with respect to reach ranges, sight lines, etc.
Area of Refuge - A safe holding area that has been designated in a Fire Safety Plan, with direct access to an exit, and is equipped with separate ventilation and communication equipment. It is a place where people can wait temporarily until they can exit safely or await further instructions or assistance during an emergency evacuation.
Arena - Refers to an enclosed, indoor venue, often circular or oval-shaped, and designed to showcase a variety of performance or sporting events (e.g., hockey, basketball, football, or soccer) in a large open space, typically surrounded by most or all sides by tiered seating for spectators. Often, the key feature of an arena is that the event space is the lowest point, allowing for maximum visibility.
Assembly Area - A room or space accommodating a group of individuals for educational, recreational, political, social, civic or amusement purposes, or for the consumption of food and drink.
Assistive Listening Systems (ALS) - Assistive listening systems (ALS) augment standard public address and audio systems by providing signals that can be received directly by persons with special receivers or their own hearing aids and which eliminate or filter background noise. The type of assistive listening system appropriate for a particular application depends on the characteristics of the setting, the nature of the program, and the intended audience. Magnetic induction loops, and infrared and radio frequency systems are types of listening systems that are appropriate for various applications. Refer to Induction Loop or Infrared Assistive Listening Systems.
Attic or roof space - The space between the roof and the ceiling of the top story or between a dwarf wall and a sloping roof.
Audible Signals - Signals that emit a distinctive sound, communication or alert to provide a warning or indicate a readiness to respond (e.g., alarm bell or signal).
Automatic Door - A door equipped with electronic sensors allowing it to be opened and triggered when pedestrians approach (e.g., typically sliding doors or swing doors equipped with guardrails for safety). See Power-Assisted Door.
Barrier - Refers to anything that prevents a person with a disability from fully participating in any aspect of society because of their disability. This can include a physical barrier, an architectural barrier, an information or communication barrier, an attitudinal barrier, or a technological barrier for example. It can also include policies and practices that result in an obstacle or hardship (e.g., systemic barrier).
Blended Curb - A connection with a slope of 1:20 (5%) or less between the level of a pedestrian walkway and the level of a crosswalk.
Board room / Conference room / Meeting room - A room used for meetings, which accommodates six or more people.
Bollard - Tpically a 900 mm high (minimum) post to mark a pedestrian path from vehicular traffic.
Braille - Braille is a system of touch reading for the blind which employs embossed dots evenly arranged to represent numbers and letters. Literary Braille, as officially approved, comprises two grades. Grade 1 Braille is in full spelling and consists of the letters of the alphabet, punctuation, numbers, and a number of composition signs that are special to Braille. Grade 2 Braille consists of Grade 1 and 189 contractions and short-form words, typically used for signage where space is limited.
Building - A structure occupying an area greater than ten square metres, consisting of a wall, roof and floor or any of them, or a structural system serving the function thereof, including all plumbing, fixtures and service systems appurtenant thereto; or a structure occupying an area of ten square metres or less that contains plumbing, including the plumbing appurtenant thereto; or structures designated in the Ontario Building Code.
Change Room - See Dressing Room.
Clear - Unobstructed.
Clear Floor Space - The amount of unobstructed floor or ground space required to accommodate a single stationary user, or a mobility device / aid, such as wheelchairs, scooters, canes and crutches.
Closed Circuit - A telephone with dedicated line(s), such as a house phone, courtesy phone or phone that must be used to gain entrance to a building or part thereof.
Closer - See Door Closer.
Common Use - Refers to those interior and exterior rooms, spaces or elements that are made available for regular and daily for use by the occupants or visitors of a facility. (e.g., common use areas of an office may include kitchens, reception areas, washrooms, etc.).
Communication - Devices that enable or enhance the ability of people to receive or transmit information, Devices and Systems usually electronically, for communication.
Comply with - Meet one or more specifications of this standard.
Cross Slope - The slope that is perpendicular to the direction of travel. Opposite of running slope.
Crosswalk - That part of a roadway at an intersection is marked for safe pedestrian crossing (e.g., by lines or other markings on the surface).
Curb Ramp - A sloped ramp surface cutting through a curb or built up to it (e.g., between the sidewalk and the road surface).
Dais - Refer to Stage.
Deaf - A term to describe people with a severe to profound hearing loss (90 decibels or greater), with little or no residual hearing. Lowercase deaf is used when referring to the medical / audio logical condition of having little or no hearing, while uppercase Deaf refers to individuals who identify themselves as deaf and share a culture and community, not just a medical condition.
Deafened - A term used to describe individuals who grow up hearing or hard of hearing and suddenly, or gradually, experience a profound loss of hearing. Late-deafened adults usually cannot understand speech without visual clues such as print interpretation (e.g., computerized note taking), speech reading or Sign Language.
DeafSpace - Deaf people inhabit a rich sensory world where vision and touch are a primary means of spatial awareness and orientation. Many use sign language, a visual-kinetic mode of communication and maintain a strong cultural identity built around these sensibilities and shared life experiences. Our built environment, largely constructed by and for hearing individuals, presents a variety of surprising challenges to which deaf people have responded with a particular way of altering their surroundings to fit their unique ways-of- being. This approach is often referred to as DeafSpace. (Source: Gallaudet University, Campus Design and Planning).
Disability - Describes a functional limitation or activity restriction caused by an impairment. Common types include: sensory (e.g., vision or hearing), mobility, physical, cognitive, learning, or mental health disabilities. Refer to the Ontario Human Rights Code for a detailed definition of disabilities.
Door Closer - A device or assembly used to open or close a door automatically.
Door Jamb - The vertical component of a door frame.
Egress (Means of) - Means of egress refers to a continuous path of travel provided for the escape of persons from any point in a building leading to a point of safety (e.g., a separate building or an exterior open space protected from fire exposure), including exits and exit routes.
Element - An architectural or mechanical component of a building, facility, space, or site (e.g., telephone, curb ramp, door, drinking fountain, seatingl, or water closet).
Elevator Lobby - The waiting area in front of an elevator.
Entrance - An access point into a building or portion of a building or facility used to enter. An entrance includes the approach, the vertical access leading to the entrance platform, the entrance door, the landing area, vestibules (if provided), the entry door or gate, and the hardware of the entry door or gate. The principal entrance of a building or facility is the door through which most people typically enter (e.g., the highest level of use).
Exit - The part of a means of egress, including doorways, that leads from the floor area it serves to a separate building, an open public thoroughfare, or an exterior open space protected from fire exposure from the building and having access to an open public thoroughfare.
Facility - All or any portion of buildings, structures, elements, improvements, equipment and pedestrian or vehicular routes located on a site or in a public right-of-way, where specific programs or services are provided or activities performed.
Fire Safety - A general term typically relating to the ability of a building or site to resist, suppress or control the onset and spread of fire and the protection of building occupants.
Fire Safety Plan - An operational plan that provides information, directions, strategies and recommendations for the safe evacuation of users during fire emergencies.
Firm Surface - Refers to a surface that does not deform under the vertical forces exerted by permitted users. Reference ASTM F 1951 Standard.
Flared Sides - A sloped surface that flanks a curb ramp and provides a graded transition between the ramp and the sidewalk. Flares bridge differences in elevation and are intended to prevent ambulatory pedestrians from tripping. Flares are not considered part of the accessible route.
FM Assistive Listening System - FM assistive listening systems are variations on the commercial FM radio. Radio signals are broadcast by an FM transmitter that is piggybacked on the sound system used in the facility. These signals are received by individual “radios”, which are small pocket-size receivers tuned to the specific frequency used in the transmission.
Foot-Candle (FC) - Refers to measurements of the visible light intensity on a surface, a distance from the light source. One foot-candle is equivalent to the illumination produced by one candle (an optical standard reference) at a distance of 305 mm (one foot). One foot-candle equals approximately ten lux. Foot-candle is the imperial measure. Refer to Lux.
Forward Approach - Where a person will make use of a service counter, drinking fountain, or any other usable element of the built environment, by positioning their body or mobility aid directly in front of and facing the element.
Glare - Often refers to uncomfortably bright light reflected from a surface, floor, window or screen. Glare occurs when one part of the environment is much brighter than the general surrounding area, causing annoyance, discomfort or loss in visual performance.
Grade - The slope parallel to the direction of travel is calculated by dividing the vertical change in elevation by the horizontal distance covered.
Graphic conventions - Dimensions that are not marked maximum or minimum are absolute unless otherwise indicated.
Ground floor - Any occupiable floorless than one story above or below grade with direct access to grade. A facility always has at least one ground floor and may have more than one ground floor, as where a split-level entrance has been provided or where a facility is built into a hillside.
Guard - A protective barrier to prevent accidental falls at openings in floors and at the open sides of stairs, landings, balconies, mezzanines and ramps. Handrail supports often act as guards.
Handrail - A component that is normally grasped by hand for support at stairways and other places where needed for the safety of pedestrians.
Hard of Hearing - A term used to describe people with a hearing loss who rely on residual hearing to communicate through speaking and speech-reading, as well as to hold conversations on the telephone. The degree of hearing loss can range from mild to profound. People who are hard of hearing can understand some speech sounds, with or without a hearing aid, and communicate primarily by speech. Persons who are hard of hearing often use hearing aids, lip reading and other assistive technologies.
Heritage facility - A facility or portions thereof designated under the Ontario Heritage Act, or identified in the inventory of heritage resources for the City of London. (See Public Heritage Facility).
Illumination - The combined amount and intensity of lighting provided, measured in foot-candles or lux.
Induction Loop Assistive Listening System - Induction loop assistive listening systems use a wire around the room to transmit an electromagnetic signal that is picked up by a small telecoil in the hearing aid. Users simply switch on this telecoil (the “T” setting) and adjust the volume of the hearing aid, if necInduction Loop Assistive Listening Systemessary. Loop systems are generally used by fewer people with hearing loss due to advances in hearing aid technology.
Infrared Assistive Listening System - Infrared assistive listening systems operate on infrared light that is beamed from one or several infrared transmitters to small, specialized receivers. There are several types of infrared receivers: stethoscope-style that dangle from the ears, a headset type that fits over the ears, and a small pocket-size type similar to the FM receiver. Where confidential transmission is essential (e.g., a court room setting), an infrared system generally is more effective recognizing transmission will be restricted within a given space.
Kilonewton (kN) - Equals 1000 Newtons.
Lavatory - A washbasin or sink used for personal hygiene.
Lux - The metric measurement for light intensity or illumination. See Foot-Candle.
Maneuvering Space - The minimum floor or ground area needed for users of mobility aids to move into or out of a place, space or along an accessible pathway or route.
Marked Crossing - A crosswalk or other identified path intended for pedestrian use in crossing a vehicular way.
May - Denotes an option or alternative.
Mezzanine or Mezzanine floor - That portion of a storey which is an intermediate floor level, is placed within the storey and has occupiable space above and below its floor.
Mobility Aids (or Devices) - A term used to encompass the variety of assistive devices used by people with mobility / physical types of disabilities, including manual and power wheelchairs, scooters, canes, and crutches.
Newtons (N) - The amount of force needed to move 1 kilogram of an object 1 meter per second squared.
Occupiable - A room or enclosed space designed for human occupancy in which individuals congregate for amusement, educational or similar purposes, or in which occupants are engaged in labor, and which is equipped with means of egress, light, and ventilation.
Open space - Large-scale tracts of land without visible evidence of residential, commercial or industrial development. These areas may be privately or publicly owned and are generally left in a natural state and not programmed for active recreation. The benefits of open lands typically extend beyond the immediate area and usually provide community-wide benefits.
Operable Control - The part of equipment or appliances that is used to insert or withdraw objects, to activate or deactivate, or adjust the equipment or appliance (e.g., a coin slot, pushbutton or handle).
Operable Portion - A part of a piece of equipment or appliance used to insert or withdraw objects or to activate, deactivate, or adjust the equipment or appliance, such as a coin slot, push button, or handle.
Park - Land that is privately nor publicly held has been developed for multiple recreational and leisure-time uses. This land benefits the entire community and balances the demands of the public for outdoor recreational facilities and other amenities, such as pathways, picnic areas, playgrounds, water features, and spaces for free play and leisure.
Passenger Loading Zone - Designated and signed area used for loading and unloading passengers into or out of a waiting vehicle.
Pedestrian Access Route - An accessible route or corridor for pedestrian use within the public right-of-way.
Pictogram - A pictorial symbol or image that represents activities, facilities, spaces or concepts.
Platform Lift - An elevating device which is used to transport a person (with or without assistive equipment) between levels on a platform. A vertical platform lift is a self-contained unit, with or without an enclosure. An inclined platform lift is used for staircases.
Power-Assisted Door - A door with a mechanism that opens the door automatically, upon the activation of a switch, button, or control. The door also remains in the “open” position for a set period of time to allow safe passage. See Automatic Door.
Private Open Space - Privately owned land areas within a subdivision, generally smaller in scale than open space, have been left free from structures, parking lots and roads. These types of areas generally benefit only the residents or employees of the particular subdivision and usually remain in private ownership.
Public Entrance - An entrance that is not a service entrance or a restricted entrance.
Public Heritage Facility - A facility or portions thereof designated under the Ontario Heritage Act, or identified in the inventory of heritage resources for the City of London and that is open and accessible to the public. (See Heritage Facility)
Public Use - Buildings, facilities, and interior or exterior rooms, spaces, sites, or elements that are made available to the public and that are typically owned, operated, or leased by the City of London.
Ramp - A walking surface with a running slope steeper than 1:20.
Retrofit - See alteration.
Running Slope - The slope that is parallel to the direction of travel is expressed as a ratio of rise to run. The opposite of cross slope.
Service Counter - A raised surface on which business is transacted. Service counters can be composed of either built-in (e.g., kiosks) or loose furniture (e.g., podiums). Other examples of service counters include: ATMs, checkout counters, self service kiosks, food vendor, and information counters.
Service Entrance - An entrance not intended for use by the public and used primarily for delivery of goods and services.
Service Room - A room provided in a building to contain equipment associated with building services.
Service space - A space provided in a facility to facilitate or conceal the installation of facility service facilities such as chutes, ducts, pipes, shafts or wires.
Shall - Denotes a mandatory specification or requirement.
Should - Denotes an advisory specification or recommendation.
Side Approach - Where a person will make use of a service counter, drinking fountain, or any other usable element of the built environment, by positioning their body or mobility aid perpendicular to the element.
Sidewalk - A public right-of-way designated for pedestrian use and typically located between the curb or roadway and the adjacent property line.
Sightline - The line of view between a person in an audience and a performance, speaker or displayed item.
Sign or Signage - A sign is a means of conveying information about direction, location, safety or form of action and in general should be designed to be clear, concise and consistent. Signage displays text, symbols, tactile or pictorial information.
Site - A parcel of land bounded by a property line or a designated portion of a public right-of- way.
Site Improvement - Landscaping, paving for pedestrian and vehicular ways, outdoor lighting, recreational facilities added to a site.
Sleeping Accommodations - Rooms in which people sleep, for example, a dormitory.
Slip-Resistant - A surface that provides sufficient frictional counterforce to the forces exerted in walking to permit safe ambulation.
Space - A definable area (e.g. room, toilet room, hall, assembly area, entrance, storage room, alcove, courtyard, or lobby).
Sprinklered - Refers to a building or any part of a building equipped with an automatic sprinkler system.
Stable Surface - Refers to a surface that does not deform or erode under the angular forces of permitted users traveling in a straight line or turning.
Stage - Refers to a space designed primarily for performances and is typically elevated from the audience seating area.
Stair System - Refers to combined elements that make up a typical stair, including steps, landings, and handrails, for example.
Storey - That portion of a building is included between the upper surface of a floor and the upper surface of the floor next to it.If such a portion of a building does not include occupiable space, it is not considered a story for the purposes of this standard. There may be more than one-floor level within a story, as in the case of a mezzanine or mezzanine.
Street Furniture - Elements in the public right-of-way that are intended for use by pedestrians, including benches, lighting fixtures, waste dispensers and paper vending machines, for example.
Structural Frame - The columns and the girders, beams, trusses, and spandrels have a direct connection to the columns and all other members which are essential to the stability of the building as a whole.
Tactile - Describes an object that can be perceived using the sense of touch, and typically provided for users with vision loss.
Tactile Walking Surface Indicator (TWSI) - A surface detectable underfoot or by a long white cane, to assist persons with low vision or blindness by alerting or guiding them. TWSI's are referred to as either tactile attention indicator (TAI) or tactile directional indicator (TDI) surfaces.
TDD - (Telecommunication Device for the Deaf): See Text telephone.
Technically Infeasible - This means, with respect to an alteration of a building or a facility, that it has little likelihood of being accomplished, because:
Temporary Structure - A facility that is not of permanent construction but that is extensively used, or is essential for public use for a period of time. Examples of temporary facilities covered by this standard include, but are not limited to, reviewing stands, bleacher areas, temporary kiosks, temporary health screening services or temporary safe pedestrian passageways around a construction site. Structures and equipment directly associated with the actual processes of construction, such as scaffolding, bridging, materials hoists, or construction trailers, are not included.
Text Telephone (TTY) - Machinery or equipment that employs interactive text-based communication through the transmission of coded signals across the standard telephone network. Text telephones can include, for example, devices known as TDDs (telecommunication display devices or telecommunication devices for deaf persons) or computers with special modems. Text telephones are also called TTYs, an abbreviation for teletypewriter.
Touch Tour - Typically refers to tours provided by museums or other cultural / arts facilities that allow users with vision loss to touch and feel objects, displays, and features, for example, to gain a sensory understanding of objects and allow individual exploration. Tactile experiences may include: replicas, models, props, and handling objects that convey one aspect of the work.
Transfer Space - An unobstructed area adjacent to a fixture or furniture, allows the positioning of a mobility aid to assist users with transferring to the fixture or furniture.
Universal Access - A broad term to reflect the intended goal of inclusion for all, based on the principles of universal design or the “design of products and environments to be usable by all people, to the greatest extent possible, without the need for adaptation or specialized design” (Ron Mace).
Universal Trail Assessment Process or UTAP - An objective method of documenting trail conditions for universal access. The UTAP:
Vehicular way - A route intended for vehicular traffic, such as a street, driveway or parking lot, within the boundary of the site.
Video Signage - Video signage refers to video devices such as televisions, computer monitors/screens, and flat panel displays that may be used to provide information (e.g., directories). Advantages of video signs include the use of motion to attract attention, and the ability to rapidly update the contentVideo Signage of the signs.
Vision Loss - This term usually refers to a progressive decrease in visual acuity. However, it can refer to the sudden onset of substantial acuity decrease or total blindness.
Vision Panel - A glazed opening in a door leaf allows people to see through to the other side without opening the door.
Walk - An exterior pathway with a prepared surface intended for pedestrian use, including general pedestrian areas, such as plazas and courts, within the boundary of the site.
Wayfinding - A term used to describe a variety of means for spatial orientation and finding your way to a destination. Wayfinding design describes a variety of means for helping people find their way, through touch, print, signage, architecture, and landscaping, for example.
Chapter 2 Common Elements
2.1 Ground and Floor Surfaces
2.2 Ramps
2.3 Stairs
2.4 Guards and Handrails
2.5 Overhanging and Protruding Objects
2.6 Tactile Walking Surface Indicators
2.7 Rest Areas
2.8 Seating, Tables and Work Surfaces
2.9 Drinking Fountains and Bottle Filling Stations
2.10 Materials and Finishes
2.11 Texture and Colour
Chapter 3 Exterior Elements
3.1 Parking
3.2 Passenger Loading Zones
3.3 Exterior Paths of Travel
3.4 Curb Ramps and Depressed Curbs
3.5 Accessibility During Construction
3.6 Site Furniture
3.7 Landscaping Materials and Plantings
Chapter 4 Interior Elements
4.1 Entrances
4.2 Doors and Doorways
4.3 Interior Accessible Routes
4.4 Elevating Devices
4.5 Washrooms
4.6 Showers
4.7 Bathtubs
Chapter 5 Controls, Systems, and Communications
5.1 Controls and Operating Mechanisms
5.2 Assistive Listening Systems
5.3 Public Address Systems
5.4 Acoustics
5.5 Security Systems
5.6 Fire and Life Safety Systems
5.7 Lighting
5.8 Signage and Wayfinding
5.9 Self-service Kiosks
5.10 Windows
5.11 Audible Pedestrian Signals
Chapter 6 Special Facilities and Spaces
6.1 Assembly Areas
6.2 Meeting and Multipurpose Rooms
6.3 Cultural and Art Facilities
6.4 Cafeteria and Dining Facilities
6.5 Kitchens and Kitchenette
6.6 Libraries
6.7 Recreational and Community Facilities
6.8 Change Rooms
6.9 Balconies and Terraces
6.10 Service Counters
6.11 Waiting and Queuing Areas
6.12 Elevated Platforms or Stages
6.13 Office Environments
6.14 Training and Teaching Spaces
6.15 Laboratories
6.16 Service Animal Relief Areas
6.17 Municipal Courts
6.18 Fire Stations
6.19 Police Stations
6.20 Child Care Facilities
6.21 Business, Mercantile and Civic
6.22 Storage, Shelving and Display Units
